V.C.E Chemistry
Year 11 Revision Notes
Mole Theory - Stoichiometry
Differentiate
between a molecule of a compound and a molecule of an element.
Name
and state the charge of the products of ionization or dissociation of molecules
Use
valencies to write the empirical (molecular) formula of compounds.
Name a
compound from its formula.
Use
valencies and formulae to write balanced molecular equations
Determine
the mass in A.M.U. of a molecule given the atomic mass of the elements involved.
A
compound is a substance formed by the chemical combination of two or more
substances
eg.
Na+ + Cl
![]() NaCl
NaCl
Using
this definition it is quite simple to differentiated between a molecule of an
element and a molecule of a compound.
A
molecule of an element is made up of only one element.
eg.
H2 , O2 , N2 , O3
Amolecule
of a compound is made up of at least two different elements, although each
molecue is a separate entity
eg.
NaCl , BaSO4 , CrPO4
Molecules
may break up to give ions when dissolved in polar solvents such as water in two
ways depending on the type of bonding in the molecule.
when ionically bonded, compounds break up
to release ions into solution with water. The water molecules tear the
ions from the crystal lattice of the compound and surround them to keep them in
solution
e.g. for sodium chloride
Na+Cl
+ nH2O
![]() Na+(H2O)a
+ Cl (H2O)b
Na+(H2O)a
+ Cl (H2O)b
or Na+Cl
![]() Na+
+ Cl
Na+
+ Cl
Not
all ionically bonded compounds dissociate (dissolve) to the same extent in water
(or other polar solvents). Those such as NaCl which dissolve and dissociate
completely are said to strong electrolytes. Those which do not dissociate
completely are called weak electrolytes.
some
covalently bonded molecules when reacted with a polar solvent such as water,
react to form ions. This process is called ionisation. Not all covalent
compounds so this. Some tend to ionise completely, some only partially, others
not at all.
e.g.
H
Cl +
H2O
![]() H3O+
+ Cl-
H3O+
+ Cl-
Hydronium
Chlroide
Ion
Ion
H2SO4
+ 2 H2O
![]() 3
H3O+ +
SO42-
3
H3O+ +
SO42-
Sulphate Ion
CH3COOH
+ H2O
![]() H3O
+ +
CH3COO-
H3O
+ +
CH3COO-
Acetate ion
(only slightly ionised)
C6H12O6
+ n H2O
![]() C6H12O6
(H2O)n
C6H12O6
(H2O)n
Glucose
(dissolves but not ionized)
The
valency of an element is a number
representing the combining (bonding) capacity of that element.
Consider
HCl H2O
CaCl2 NH3
AlCl3
CH4 CCl4
Pb3(PO4)2
If
H has a valency of +1 in HCl, then Cl is 1
Ca
= +2 , Al = +3 , C = +/ 4 , O = 2 , N = 3 , Pb = +2 , PO4 =
3
i)
AlCl3
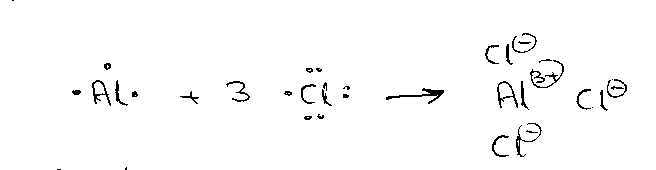
Al
donates 3 electrons so it has a valency of +3
Cl
accepts 1 electron so it has a valency of 1
Electrovalency
is the Number of Electrons transferred
ii)
H2O
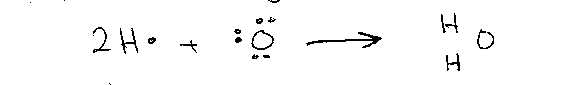
O
share 2 electrons so has a valency
of 2
H
shares 1 electron so has a valency of 1
Covalency
is the Number of Electrons shared
The
numerical values of the two types of valency are in general is the same and only
differ depending on whether the compound is covalent or ionic. Knowing the
valencies of each element and also ionic radical such as nitrate (NO3-) ,
sulphate (SO4 2- ), it is possible to determine the
empirical formula of a compound by the following steps
1)
Determine
whether the compound is ionic (electrovalent) or covalent (ie metal / non-metal
, non-metal / non-metal or metal / metal)
2)
Determine
the relative valencies of each species present
3)
Balance
the valencies in all parts of the molecule to give a nett valency of zero.
e.g.
i) NaCl
metal / non-metal ΰ ionic ccompound
Na = +1
Cl = -1 (electrovalencies)
Net valency = zero
ii) Nitrogen Hydride
(Ammonia)
non-metal / non-metal
ΰ covalent
N = 3 , H = 1
(covalencies)
NH3 ΰ nett valency = zero
When
naming a compound from its formula, one must follow these two steps
i)
Divide
the compound into its relevant species
ii)
Name
the compound according to its components
This
involves committing to memory the names of various species
A
balanced equation shows that in a chemical reaction, atoms undergo re
arrangement, as bonds are broken and new bonds formed between different atoms.
The equation is written to summarize observed data and the equations must
conform to the changes which are observed to take place. In a balanced equation,
equal numbers of atoms of each element appear on both sides of the equation.
There are three
basic steps to follow when writing a balanced chemical equation.
1)
Determine
from the information given what the reactants are what the products are
2)
Write
a skeletal or unbalanced equation eg.
Reactants ΰ
Products
3)
Using
the skeletal equation, balance all numbers of atoms to give a balanced equation.
NOTE
use valencies to determine whether each product is neutral or not
To
determine the Relative Molecular Mass of a molecule given the atomic masses of
its constituents, one only has to add up the masses of it constituent elements
The
empirical formula of a compound is the formula which represents the simplest
ratio of the numbers of the respective atoms or ions on the compound